Lecture 9
Evaluating Trade-Offs: Benefit–Cost Analysis and Other Decision-Making Metrics
September 16, 2024
Benefit–Cost Analysis and Other Decision-Making Metrics
Normative Criteria for Decision Making
Comparing Benefits and Costs Across Time
Time is an important factor in many environmental and resource policy decisions
Present value concept allows comparison of benefits and costs across time
Present value incorporates the time value of money
Present value interpretation:
- Amount needed now to generate the future stream of net benefit
- Makes future values comparable to current values
Normative Criteria for Decision Making
Comparing Benefits and Costs Across Time
- Present value of a one-time net benefit (\(NB_{n}\)) received \(n\) years from now is \[
PV[NB_{n}] \,=\, \frac{NB_{n}}{(1 \,+\, r)^{n}}
\] \(\quad\) - \(r\): the interest rate
\(\quad\) - \(B_{0}\): the amount of net benefits received immediately
Normative Criteria for Decision Making
Comparing Benefits and Costs Across Time
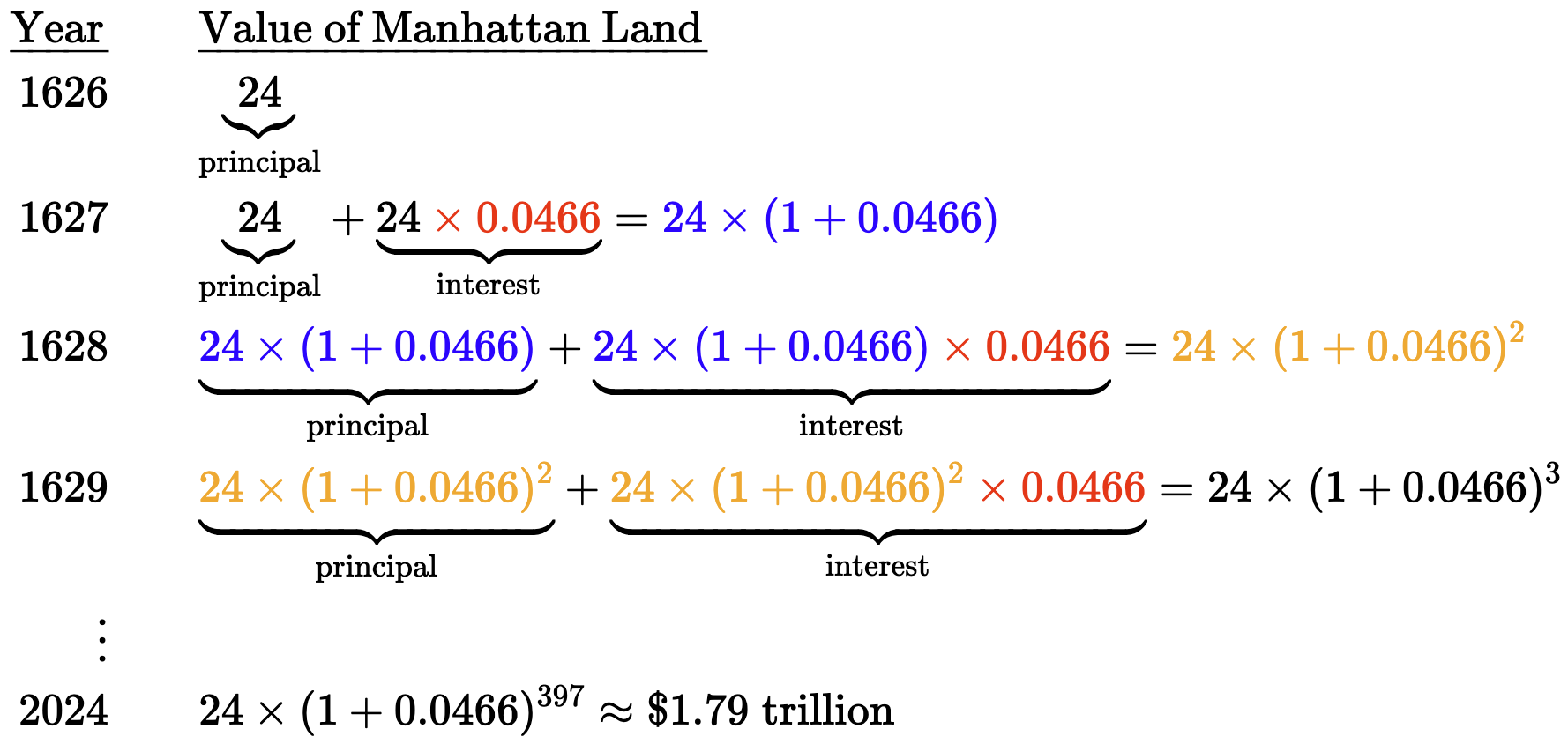
- The funds used to purchase Manhattan Island for $24 in 1626!
Normative Criteria for Decision Making
Comparing Benefits and Costs Across Time
- The present value of a stream of net benefit \(\{NB_{0}, \cdots , NB_{n} \}\) received over a period of \(n\) years is
\[ PV[NB_{0},\cdots,NB_{n}] \,=\, \sum_{i=0}^{n}\frac{NB_{i}}{(1 \,+\, r)^{i}} \]
\(\quad\) - \(r\): the appropirate interest rate
\(\quad\) - \(B_{i}\): the amount of net benefits received in the \(i^{\text{th}}\) period
- Discounting: process of calculating present value
- The rate \(r\) is referred to as the discount rate.
Normative Criteria for Decision Making
Comparing Benefits and Costs Across Time
- Decision rule for evaluating actions:
- Calculate present value of net benefits
- If present value > 0, support the action
- If present value < 0, do not support the action
- Present value allows for rational comparison of different time-based scenarios in economic decision-making
Normative Criteria for Decision Making
Comparing Benefits and Costs Across Time
Normative Criteria for Decision Making
Dynamic Efficiency
An allocation of resources is said to satisfy the static efficiency criterion if the economic surplus from the use of those resources is maximized by that allocation.
An allocation of resources across \(n\) time periods satisfies the dynamic efficiency criterion if it maximizes the present value of net benefits that could be received from all the possible ways of allocating those resources over the \(n\) periods.
Allows for comparison and optimization of resource use over time, rather than just at a single point in time
Helps in making decisions about resource use that have long-term implications
Normative Criteria for Decision Making
Dynamic Efficiency
- Question
- Consider the role of discount rates in problems involving long time horizons such as climate change.
- Suppose that a particular emissions abatement strategy would result in a $500 billion reduction in damages 50 years into the future.
- Given the following two present values of such damage, which one corresponds to the 2 percent discount rate, and which one to the 10 percent discount rate?
- $4,259,275,640
- $185,763,941,063